Definition of Basic Parameters for NTC Thermistor Products
A Thermistor is a semiconductor component highly sensitive to temperature, with its resistance value changing significantly in response to temperature variations. Based on their temperature coefficient, thermistors are classified into Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) thermistors and Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC) thermistors.
NTC thermistors are used for temperature measurement, temperature control, and temperature compensation, and are referred to as temperature sensors.
PTC thermistors are used for temperature measurement and control, and can also function as heating elements while simultaneously acting as a "switch." They combine the three functions of a sensing element, heater, and switch, and are thus called "thermal switches."
NTC thermistors, short for Negative Temperature Coefficient, exhibit a significant decrease in resistance as temperature increases. Utilizing this characteristic, NTC components are commonly used in small household appliances for soft-start circuits, automatic detection, and control circuits.
PTC thermistors, short for Positive Temperature Coefficient, exhibit a significant increase in resistance as temperature rises. This property is often utilized in automatic control circuits.
NTC thermistors are ceramic semiconductor thermal sensing crystals primarily sintered from metal oxides such as manganese, cobalt, and nickel. Their zero-power resistance decreases as the component's own temperature increases.
A thermistor is a heat-sensitive semiconductor resistor whose resistance value changes with the component's own temperature.
Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC) Thermistor
Zero-Power Resistance (RT)
The DC resistance value measured at a specific temperature (T) when the power consumed by the thermistor is extremely low (to the point where a further decrease in power would cause a resistance change rate of less than 0.1%).
Material Constant (B Value)
The B value is calculated using the following formula based on resistance measurements at two specific ambient temperatures (in Kelvin, K):
B = Ln(R1/R2) / (1/T1 - 1/T2)
The B value for NYFEA Nyfea products is typically determined at T1=298.15K and T2=323.15K or 358.15K.
Generally, B values range from 2000 to 6000K. A higher B value indicates a greater resistance change rate per 1°C.
Dissipation Coefficient (δ)
The power required, under specific ambient conditions, to raise the temperature of an NTC thermistor by 1°C through self-heating, usually expressed in mW/°C. It can be calculated using the formula:
δ = V × I / (T - T0)
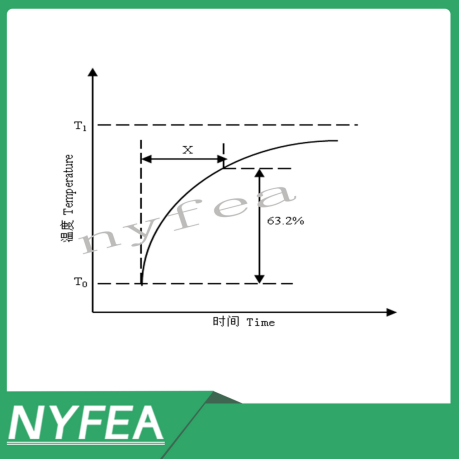
Thermal Time Constant (τ)
Under zero-power conditions, when the ambient temperature of the thermistor changes abruptly, the time required for the thermistor element to change by 63.2% of the temperature difference between its initial temperature (T0) and its final temperature (T1). It is usually expressed in seconds (s).