PTC Thermistor (Chip Type / Surface Mount)
A Thermistor is a semiconductor component highly sensitive to temperature, classified into Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC) thermistors and Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) thermistors.
NTC thermistors are used for temperature measurement, control, and compensation, functioning as temperature sensors.
PTC thermistors are used for temperature measurement and control, can also serve as heating elements, and simultaneously act as a "switch," combining the three functions of sensing element, heater, and switch, hence referred to as a "thermal switch."
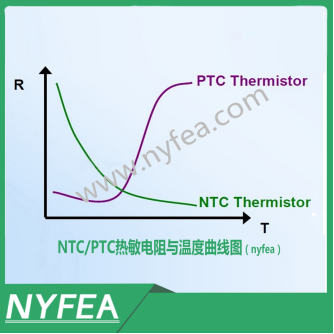
NTC Thermistor: Negative Temperature Coefficient. Resistance decreases as temperature increases;
PTC Thermistor: Positive Temperature Coefficient. Resistance increases sharply when temperature rises above the switching temperature point;
CPTC: Ceramic Positive Temperature Coefficient Thermistor, is a type of thermistor designed using semiconductor ceramic materials. The primary material is barium carbonate, with small additions of rare earth elements, acceptor elements, and glass additives, sintered at high temperatures to form a temperature-sensitive semiconductor resistor. It exhibits low resistance below the Curie temperature, but when the temperature exceeds the Curie point, the resistance increases stepwise with rising temperature. It is used for overheat sensing in circuits, providing both overheat and overcurrent protection.
Beyond industrial temperature measurement and control, PTC thermistors can also function as heating elements while acting as a "switch," integrating the three roles of sensing element, heater, and switch, making them "thermal switches."
Overheat Protection: Due to the sharp resistance change induced by temperature variation, PTC thermistors connected in series within a circuit enable precise overheat detection across multiple zones. This can be applied for overheat sensing in FETs, power ICs, and other heat-generating areas.
Overcurrent Protection: When abnormal current flows through, the PTC heats up abruptly, and its resistance rapidly increases to a high-impedance state, thereby limiting or blocking the current to protect the circuit from damage. Once the current normalizes, the PTC returns to its initial low-resistance state, and the circuit resumes normal operation. Its working principle is similar to a fuse but offers reusability.
Surface Mount PTC Thermistors (SMD Ceramic Positive Temperature Coefficient Thermistors) are chip-type components manufactured using ceramic materials known for excellent reliability and performance. They feature high reliability and fast protection, enhancing device safety and enabling maintenance-free operation. Compared to Polymer PTC (PPTC) components and chip resistors with similar characteristics, ceramic SMD PTC thermistors offer higher reliability, minimal electrical parameter shifts after mounting, and a long service life. This helps customers reduce device size and improve performance.
Features of C PTC SMD Thermistors:
1. Glass-encapsulated ceramic body provides excellent moisture resistance, high reliability, and stability;
2. Small size, lead-free design, excellent solderability, suitable for high-density surface mounting;
3. Reduces the number of IC ports required, facilitating device miniaturization;
4. Good noise immunity achieved by utilizing the characteristic of rapid electrical impedance change.
Applications of C PTC SMD Thermistors:
1. Overheat Sensing: Overheat sensing for power transistors, power LEDs, and power ICs in switching power supplies and hybrid circuits;
2. Overheat sensing in audio-visual equipment like LCD TVs, digital cameras, and audio systems;
3. Overheat sensing in information technology devices such as computers, printers, scanners, and copiers;
4. Overheat sensing in communication equipment including fax machines, mobile phones, headsets, and base stations;
5. Overheat sensing in automotive electronics like instrument clusters, engine control ECUs, and ABS systems;
6. Overheat sensing in household appliances and electronics such as refrigerators, air conditioners, washing machines, and lighting equipment.

