Understanding Near Field Communication (NFC) in One Article
Near Field Communication (NFC) is developed based on contactless Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology combined with wireless interconnection technology.
It is an emerging technology that enables devices equipped with NFC (such as mobile phones) to exchange data when they are brought close together. Evolving from the integration of contactless RFID and interconnection technologies, NFC integrates an inductive card reader, inductive card, and peer-to-peer communication functionality on a single chip. This enables mobile terminals to implement applications such as mobile payments, electronic ticketing, access control, mobile identity recognition, and anti-counterfeiting.
Key characteristics of Near Field Communication technology are as follows:
(1) A wireless communication technology for secure short-range communication (within 10cm).
(2) RF Frequency: 13.56MHz.
(3) RF Compatibility: ISO 14443, ISO 15693, Felica standards.
(4) Data Transfer Rates: 106 kbit/s, 212 kbit/s, 424 kbit/s.
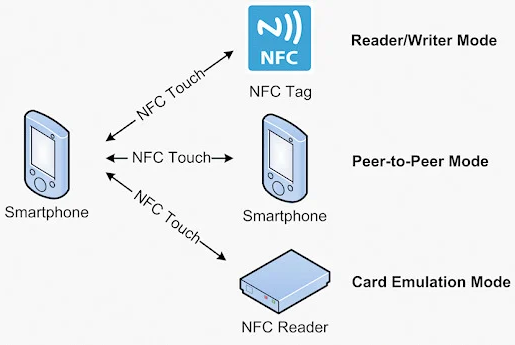
Primary NFC Applications:
Payment Applications
NFC payments primarily involve virtualizing an NFC-enabled mobile phone into applications such as bank cards or transit cards.
Security Applications
NFC security applications mainly involve virtualizing the phone into access cards or electronic tickets. Virtualizing an access card with NFC means writing existing access card data into the phone's NFC chip. This allows the phone to function as an access card, eliminating the need for a physical smart card. This not only makes the configuration, monitoring, and modification of access permissions very convenient but also enables remote changes and configuration, such as temporarily issuing access credentials when needed.
Tag Applications
NFC tag applications involve writing information into an NFC tag. Users can then instantly access the relevant information by simply tapping their NFC-enabled phone on the NFC tag.
Advantages of NFC:
NFC enables high-speed data transfer, with rates up to 424 Kbps.
NFC supports bidirectional communication, allowing simultaneous transmission and reception of data.
NFC enables highly secure data transmission due to its very short effective range.
NFC can be used for applications such as access control, asset management, and data collection.
NFC can be utilized for implementing applications like Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR).

